Star Life Cycles - Sun-sized Stars
Stars and NebulaeIndex
Interstellar Clouds Questions Credits Links Michael Gallagher August 2002 July 2007 |

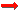
If the gas supply is sufficiently large, a sun-sized star forms. A sun-sized star supports nuclear fusion at a steady rate for billions of years. When all fusible hydrogen is exhausted, fusion of other elements begins, causing the star to expand into a Red Giant. As the supply of fusible elements is exhausted, the tenuous outer atmospheres drifts off into surrounding space to form a cloud of dust and gas called a Planetary Nebula. When all nuclear burning ceases, all that remains of the star is a very dense, very hot, spent core - a White Dwarf, an object with a sun-like mass condensed into an earth-sized body. Sun-like Star Details Mass: 0.5 to 9 Suns Surface Temperature: 5,000° to 7,000° K Lifetime: Billions of years. End point: White dwarf and planetary nebula. |