Star Life Cycles - Red Dwarfs
Stars and NebulaeIndex
Interstellar Clouds Questions Credits Links Michael Gallagher August 2002 July 2007 |
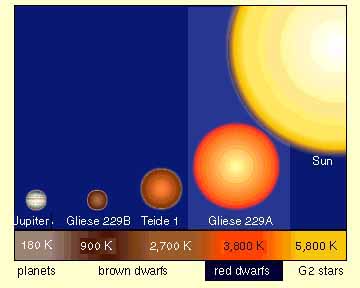
After Edward Martin et Al, American Scientist 1997 Red dwarfs have accumulated enough gas to sustain full nuclear fusion. The rate of fusion is slow - a Red Dwarf's hydrogen supply will last for trillions of years. Red dwarfs are the most plentiful stars - they account for half the stellar mass of the galaxy. They are very dim - their detection requires a telescope. The closest star to the Sun, Proxima Centauri, is a Red Dwarf - although it is only 4.2 light years away, it is much too dim to be seen by the unaided eye. Red Dwarf Details Mass: 0.08 to 0.5 Suns (80 to 500 Jupiters) Surface Temperature: 2,500° to 5,000° K Lifetime: Trillions of years. End point: Once fusion ceases, gradual loss of heat and slow fade to a dark body. |